| Zefram Laboratories LLC |
| About | Portfolio | News | Contact |
| Biomedical Instrumentation | |
 |
Multiple Particle Tracking Software |
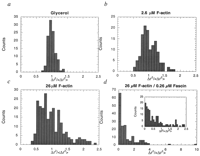
| Multiple Particle Tracking (MPT) captures the trajectory of a large number of individual fluorescently-labeled microspheres embedded. It then uses the trajectory data to compute the visco-elastic properties of the sample and to quantify the spatial distribution of those properties. Our implementation of the Multiple Particle Tracking software allows for fast, convenient, and quantitative multiple-particle tracking (MPT) measurements. MPT studies provide a strong complement to traditional biophysical methods (rheology, microscopy, spectroscopy, and light scattering) for the characterization of the properties of actin filament networks in vitro. An application of this technique using our software is presented in the Biophysical Journal. | |
| Software | |
|
|
Custom Chat Software |
|
The CustomChat(TM) server is a
robust customizable real time multithreaded HTTP chat
server. The server is a standalone Java application that
allows any HTML client to access all of the chat features
without downloading an applet, or a plug-in. We helped CustomChat(TM) to refactor their product to be more robust and extensible, to add additional product features such as remote database connectivity, and to increase server capacity to more than 4 times that of their our closest competitor. In addition, we developed a design and an implementation plan for a clustered version of their server for "Stadium" chats. |
|
 |
Smart Science |
| Smart Science is an online interactive science laboratory where students can conduct tele-experiments. Smart Science currently offers six modules targeted to ninth grade physical science. Its patent-pending use of real experiments provides a superior learning experience. We assited paracom by designing and constructing an experimental apparatus for one of their modules. | |
| Ocean Engineering | |
 |
MIT Project ORCA |
| Project ORCA is an MIT student group founded in 1998 by three current Zefram Labs Engineers. The ORCA team builds Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) for the AUVSI competition. Although graduated now, members of Zefram labs continue to be involved in the project, and have helped the team to win first place three times. For details on the project or the competition please visit web.mit.edu/orca/www. | |
|
COMING SOON |
Acoustic Direction Finder |
| The ORCA ADF is an underwater acoustic direction finder that responds to pings in the 20-40 kHz band. Each time it receives a ping, it transmits a NMEA-format string containing the direction, intensity, and frequency of the ping over its RS-232 port. The ORCA ADF uses four Reson TC4037 spherical probe hydrophones, mounted in a square array. An Analog Devices 2189M digital signal processor determines the direction of the input signal using the first-arrival method and pair-wise cross-correlation. | |
| Electrical Engineering | |
 |
AOPS |
|
AOPS is a modular PC-based small business PBX system. The system supports up to 256 internal extensions and up to 16 tie lines to the public switched telephone network. The system has a mapping of virtual to physical extensions, voice mail, call forwarding, system-wide transfer and call management features, and long distance accounting. The system has a simple software interface, which allows the administrator of the system to specify custom behaviors for the system using the C programming language. |
|
 |
Rhythm Tree |
|
The Rhythm Tree is the world’s largest electronic drum kit. The Rhythm tree is a part of the Brain Opera, an interactive musical exhibition which is currently on display at the House of Music in Vienna, Austria. The Rhythm Tree has 320 drum pads, which act as input devices for the system. Each drum pad contains a piezoelectric sensor, a PIC microcontroller, an LED, and a RS-485 interface. The drum-pad circuits are potted in a semi-transparent rubber and mounted on a stainless steel frame. Each string of 32 pads connects to a concentrator unit, which converts the RS-485 signals to MIDI. Each group of five strings connects to a PC through a MIDI merger and MIDI interface card. The computer receives signals from the drum-pads and synthesizes music in response, which is played through a distributed set of speakers. |
|
 |
Digital Simulator |
| Digital Simulator is a visual digital logic simulator intended for educational use. Using a schematic-capture editor, students can draw circuits containing logic gates, flip-flops, memory, buttons, and LED’s. The student can simulate and interact with the circuit, and can debug it using an on-screen logic analyzer. To try digital simulator, go to http://web.mit.edu/ara/www/ds.html | |
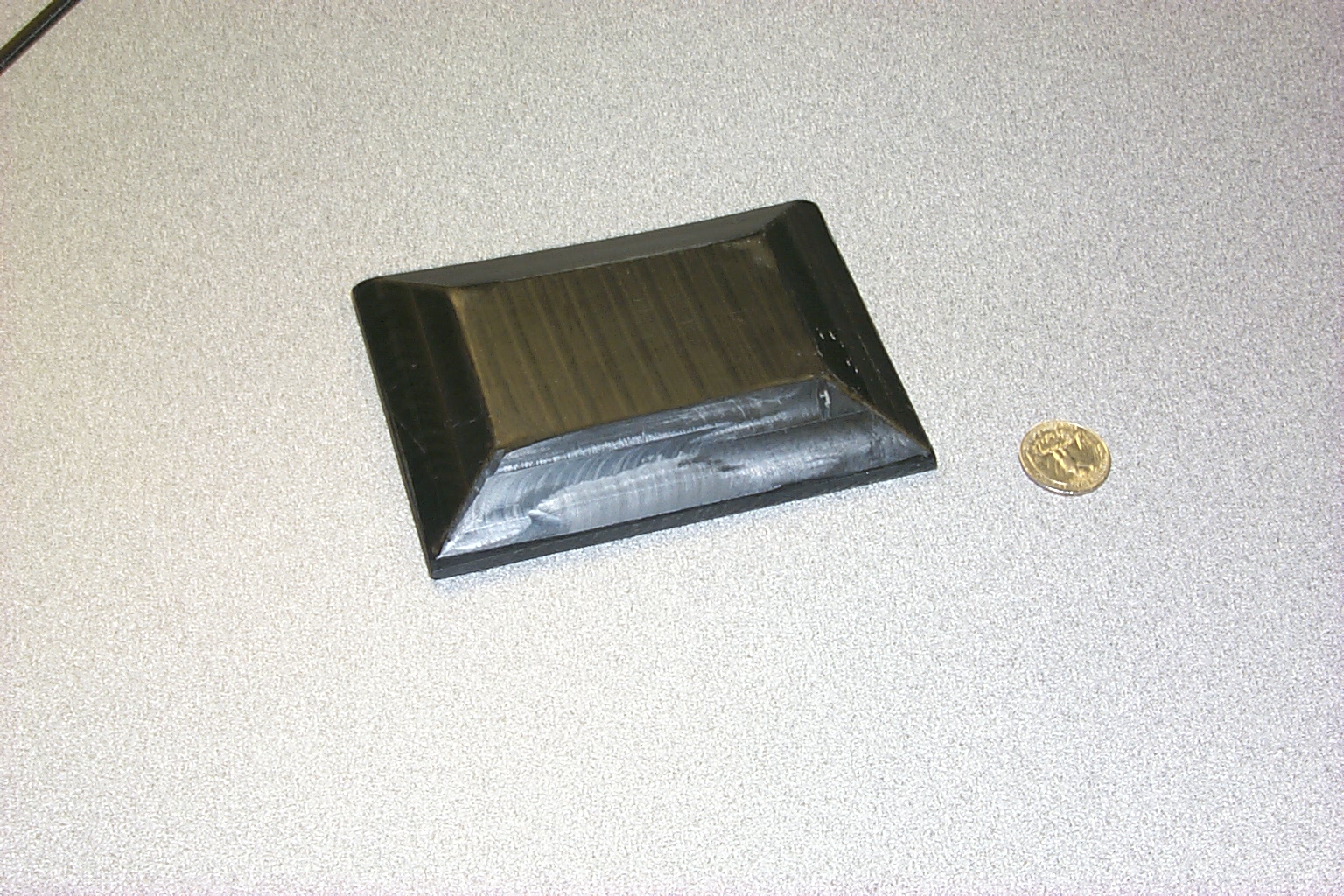 |
Ultra Low Power Wireless Traffic Sensor (Patent Pending) |
|
The ultra-low power wireless traffic sensor is a device intended to be used to instrument a roadway for Intelligent Transportation Systems. The sensor package counts passing vehicles, measures the average roadway speed, and detects ice and water on the road. Clusters of sensors can transmit this information in near real-time to wired base stations for use controlling and predicting traffic, and in clearing road hazards. The sensor package draws a maximum time-averaged current of 17mA from an internal lithium battery, allowing it to operate in the roadbed for at least 10 years without maintenance. The nodes cost well under $30 to manufacture, and can be installed without running wires under the road, facilitating wide deployment. Unlike many other types of traffic sensors, these sensors count vehicles in bumper-to-bumper traffic just as well as in widely separated traffic. The devices detect vehicles by detecting the perturbations in the Earth’s magnetic field caused by the vehicles. They measure this perturbation using an anisotropic magnetoresistive magnetic field sensor. The radio transmitters in the sensor are frequency-agile, and the sensors use a randomized sparse TDMA protocol, which allows several transmit-only devices to share a channel. The sensor package includes a custom-designed, compact, broadband, inexpensive printed circuit microstrip antenna for the 915 MHz U.S. ISM band. We built a prototype sensor package, and installed it in a pothole in a city street. We used the sensor to monitor the traffic flow rate during free-flowing traffic and a traffic jam. |
|
| Mechanical Engineering | |
 |
Injection molded and thermoformed yo-yo's |
| Zefram Labs has experience in a variety of mass production processes. In order to manufacture 100 plastic toy yo-yo's, injection molding and thermoforming processes were selected. The yo-yo body was designed with consideration given to mass distribution and dynamics, human factors, and cost of manufacturing. A stylish graphic was also incorporated into the design. The parts were designed using the 3D modeling programs ProEngineer and SolidWorks. The molds were cut out of aluminum stock, using MasterCAM to generate G-CODE to the control CNC milling machines and lathes. The molds were used in injection molding and thermoform machines to press out plastic parts in a variety of colors. The completed yo-yo consisted of 8 parts (including the string) that could be assembled by hand in less than a minute. | |
 |
Fluid Writer |
| The Fluid Writer is a research prototype of a multi-material three-dimensional printer. It has four precision-metering fluid dispensing heads, each of which is connected to a fluid reservoir. The heads are mounted on a three-axis linear motion stage. The machine also includes a high intensity pinpoint ultraviolet light source, to selectively cure UV-curable materials, and a large infrared oven to cure heat-curable materials. Associated software takes in a print configuration script and a set of RS-274X Gerber files describing the geometry of each layer, and controls the linear motion stage, dispensing equipment, and curing equipment to create the desired part. The Fluid Writer has been used to print a variety of multi-material parts, including a working linear motor | |
Copyright (C) 2002 Zefram Laboratories, LLC